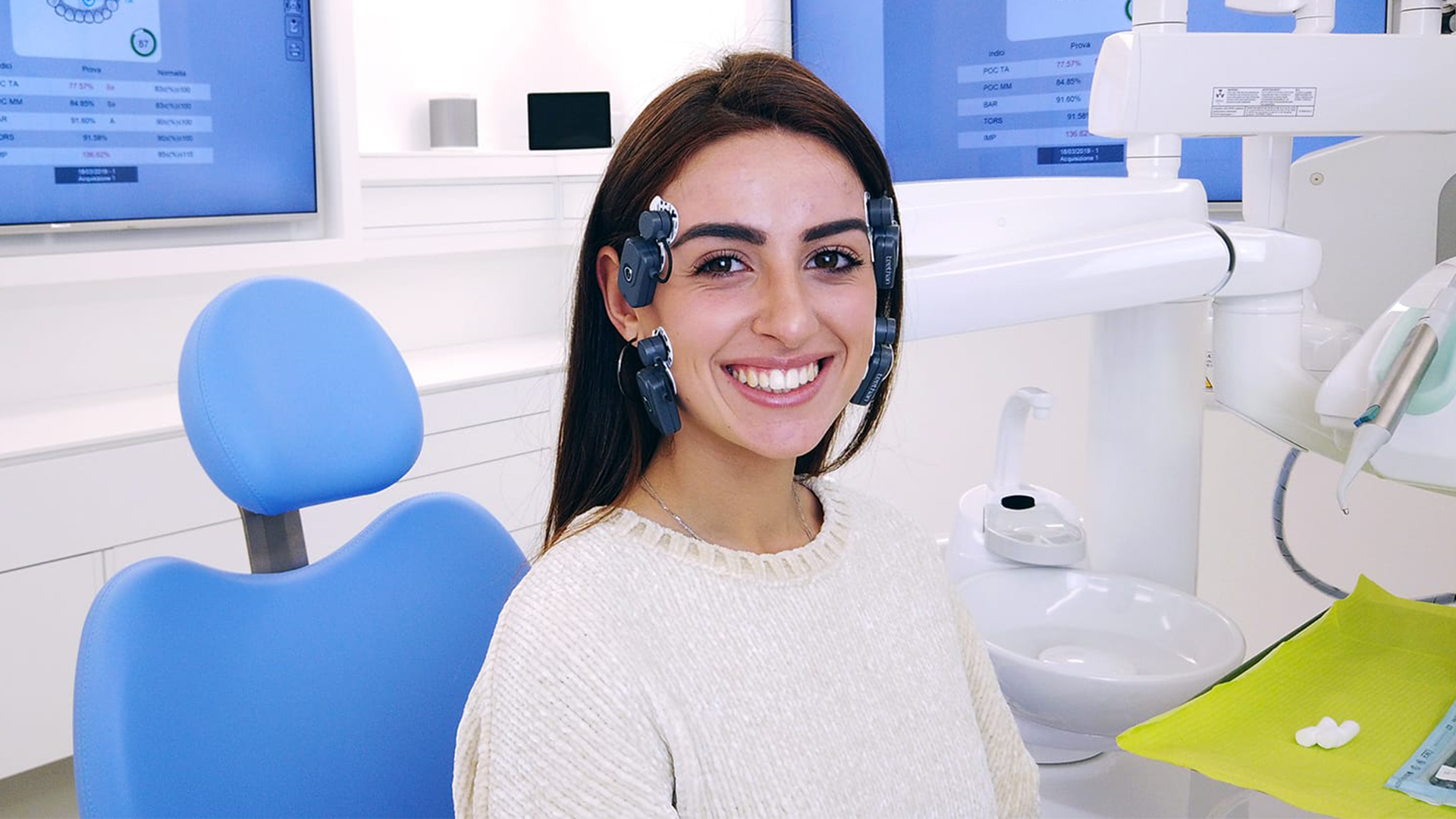
5 reasons to get Teethan in your dental practice
10 May 2021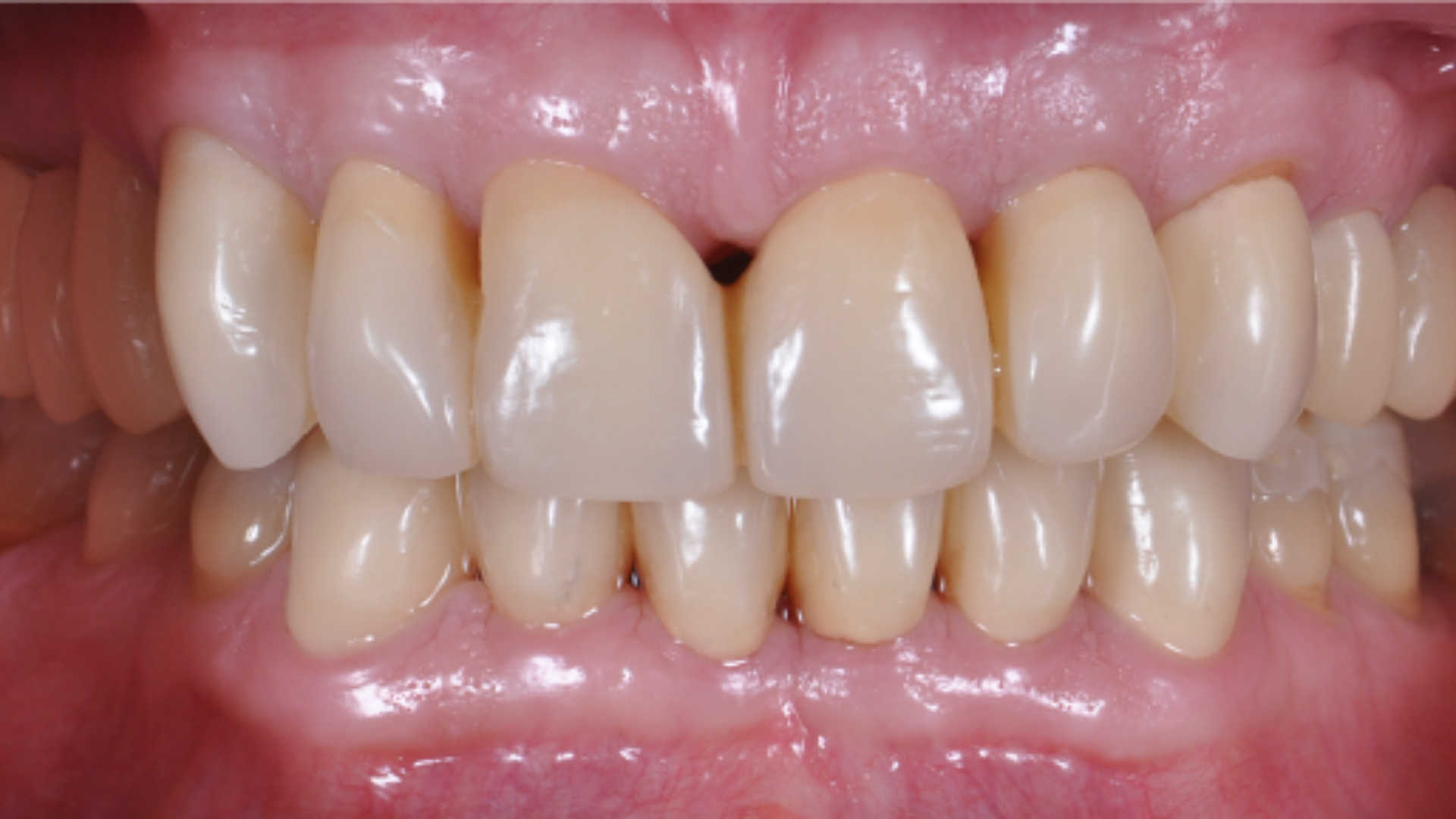
Complete rehabilitation with restoration of the vertical dimension of the lower third of the face
17 September 2021Case presentation
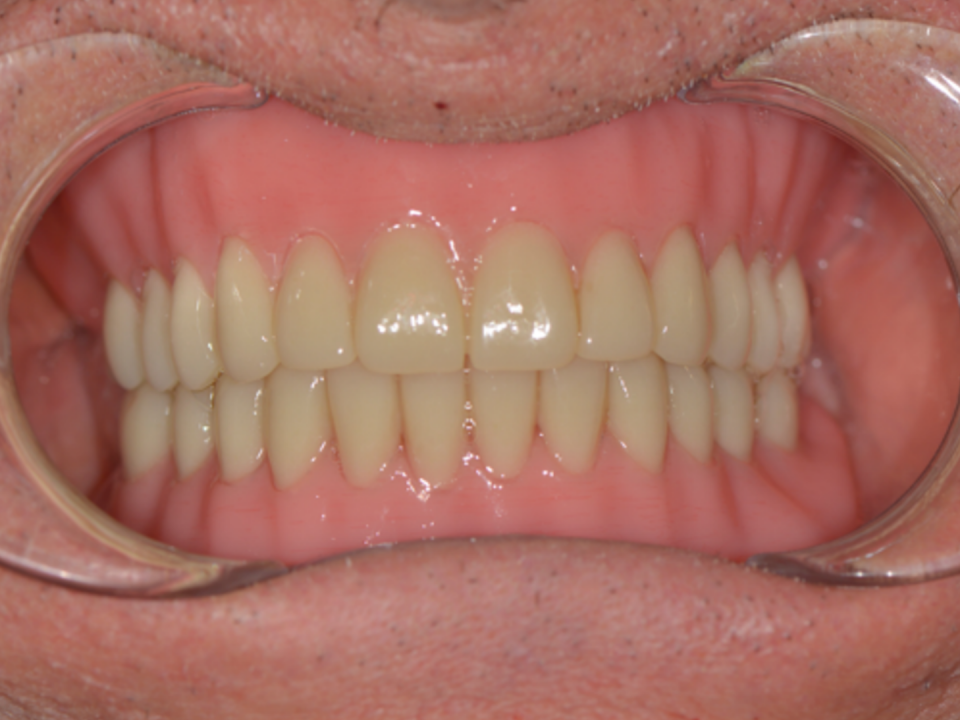
This clinical case is related to a total maxillary implant-supported rehabilitation. The patient at baseline is characterized by a complex situation from a functional point of view, due to compromised teeth and two incongruous prosthesis, that consequently cause a strong social discomfort. Teethan is used as a planification tool to allow a proper rehabilitation process design. The draft prosthesis is used for a fixed period of time, in which masticatory muscle activity is monitored periodically in order to decide how the definitive prosthesis should look like. Long term follow-up showed – by electromyographic evaluation – the achievement of a functional masticatory stability.

Pre-surgical treatment
The first step for the definition of a proper therapeutic plan and surgical intervention is aesthetic analysis, in order to define the optimal outcome. To do so, the team collected all photographic records of the baseline intra-oral condition. In this instance, the most appropriate solution consisted of rehabilitating through both upper and lower arch implants. A first functional evaluation was performed wearing prosthesis, the results of which showed a less negative situation than expected, probably due to compensatory and adapting mechanisms. Nevertheless, corrections were indispensable. An occlusal test performed using waxes for registration helped the medical equipe define the space boundaries and vertical dimension.

The information collected was then communicated to the laboratory which, using the occlusal wax as a guide, proceeded with the realization of the two draft prosthesis.

Surgery
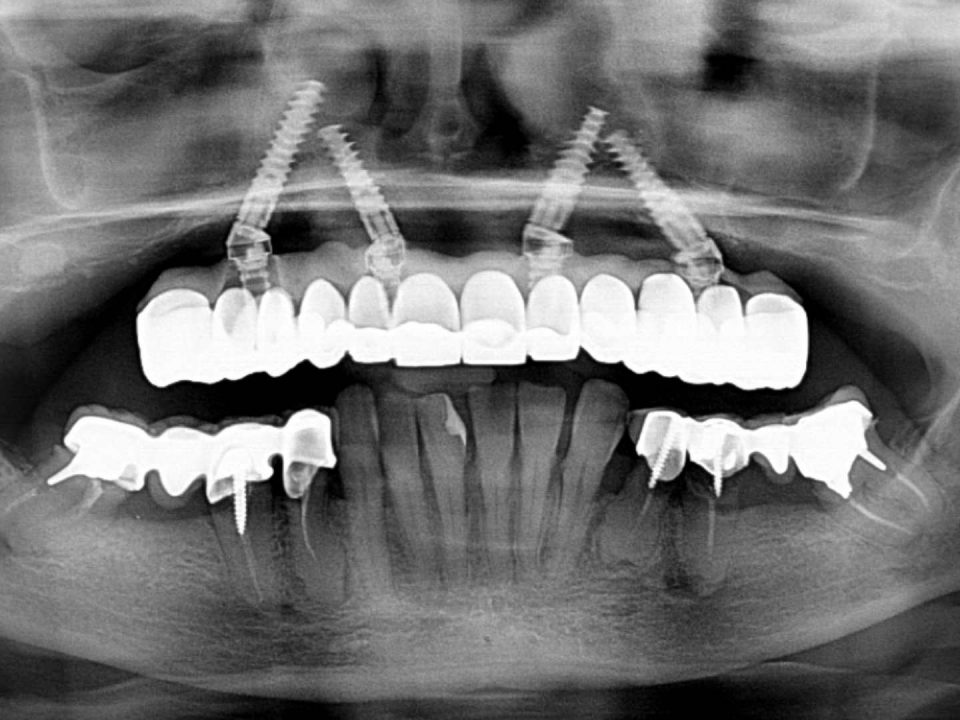
The patient was rehabilitated with two methodologies with high rates of success: all-on-4 for the upper arch and TrefoilTM for the lower arch. The latter includes the use of preformed guides that allow to insert it – with a standardized placement – inside the jaw. The advantage of this procedure is that, once the implants are in place, the prothesic structure is to consider definitive. In a six months period, necessary changes can be made, indeed, without creating further structures.



Results

Post surgical treatment
Post-surgical radiography: titanium structure of the TrefoilTM prosthesis in the lower arch.


1st Teethan evaluation: 7 days after intervention
When using Teethan for post-operative check, the values of occlusal indexes show a good normalization. The fact that the Impact index has a lower value than normality needs further elucidation, while the presence of non-normal TORS value is worrying. Therefore, in order to fix the detected suboptimal condition, a mild occlusal treatment is performed and monthly monitored.
When using Teethan for post-operative check, the values of occlusal indexes show a good normalization. The fact that the Impact index has a lower value than normality needs further elucidation, while the presence of non-normal TORS value is worrying. Therefore, in order to fix the detected suboptimal condition, a mild occlusal treatment is performed and monthly monitored.

2nd Teethan evaluation: 3 months after intervention
Results show an improvement both of Impact index and TORS indexes, corroborating the pre-surgical choice in terms of vertical dimension. The anterior barycenter is a common characteristic in this phase of treatment as the all-on-4 methodology doesn’t involve any posterior support, which can lead to a shift of the occlusal barycenter with relative alteration of masseter activity.
Results show an improvement both of Impact index and TORS indexes, corroborating the pre-surgical choice in terms of vertical dimension. The anterior barycenter is a common characteristic in this phase of treatment as the all-on-4 methodology doesn’t involve any posterior support, which can lead to a shift of the occlusal barycenter with relative alteration of masseter activity.

3rd Teethan evaluation: 6 months after intervention
In this phase it is possible to proceed to the planning of the definitive prosthesis. The possible choices are two: either to confirm the occlusal set-up and vertical dimension or to make changes in these parameters. The assessment performed with Teethan showed a good overall normalization of masticatory activity, while, specifically, masseter activity is still a bit altered due to the lack of posterior support. Indexes remain unchanged also in terms of vertical dimension.
In this phase it is possible to proceed to the planning of the definitive prosthesis. The possible choices are two: either to confirm the occlusal set-up and vertical dimension or to make changes in these parameters. The assessment performed with Teethan showed a good overall normalization of masticatory activity, while, specifically, masseter activity is still a bit altered due to the lack of posterior support. Indexes remain unchanged also in terms of vertical dimension.
Definitive prosthesis
In questo caso viene confermato il progetto protesico già in essere e funzionalizzato nei 6 mesi precedenti, mantenendo lo stesso set-up occlusale. Viene presa unaIn this clinical case, the draft prothesis is confirmed and the same occlusal set-up is kept. The only modification is the addition of the posterior support. nuova impronta, si realizza la struttura in titanio anche per l’arcata superiore e si confeziona la nuova protesi superiore con l’aggiunta del supporto posteriore dei sesti.


4th Teethan evaluation: 1 week after definitive prosthesis

Post-operative radiography

Consequently, to the addition of back support, the asymmetry due to the posterior activity of the masseters is almost completely solved.
Follow up
The patient undergoes a visit every six months and then once a year. In these occasions Teethan is used to perform a functional assessment to check on the rehabilitation implant.

Teethan evaluation: 2 years after follow-up
From the evaluation, it emerges that the Impact index has largely improved and that the barycenter has moved anteriorly. This information could mean that there’s a loss in posterior vertical dimension. In this case Teethan helped to identify the presence of wear facets, which can be responsible for the loss of prosthesis balance in time.

Fortunately, the methodology of choice allowed an easy intervention. Thanks to the use of composite teeth, the damage can be restored by adding composite to the wear facets and by retouching contacts based on occlusal balance information given by Teethan.
Keeping functional control in this kind of rehabilitation is fundamental, because the loss of proprioception can lead to the wearing of posterior structure which, in turn, can cause prosthesis’ fractures.
Conclusion
The case was concluded with two total prosthesis on implant. The follow-up checks where performed at 3-6-12-24 months. In the 12 months follow-up EMG-driven occlusal corrections were made in order to keep the functional performance of the prosthesis. After 2 years follow-up, Teethan showed the presence of wear facets and functional imbalance, both corrected.
Teethan's support
Teethan was fully integrated in the workflow to allow a functional control of the rehabilitation, which is both easy to interpret for the practitioner and minimally invasive for the patient. Thanks to Teethan it was possible to speed up the workflow and keep the patient’s functionalities under control in both short and long term. Teethan provides a valid support to this kind of activity, so much so that prosthesis issues greatly decreased, improving daily clinical practice and providing an extremely valid communication tool to talk to patients about topics which otherwise would be too complex.