TMJOINT IS AN INNOVATIVE TOOL FOR THE FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS OF DENTAL OCCLUSION. IT ALLOWS TO EVALUATE THE ACTIVITY OF THE MAIN MASTICATORY MUSCLES, ANTERIOR TEMPORALIS AND MASSETER, WITH THE POSSIBILITY TO EVALUATE ALSO STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID AND TRAPEZIUS MUSCLES OF THE CERVICAL REGION.

Four protocols
4-probes Occlusal Test (Static)
It compares two maximum intercuspation tests, lasting 5 seconds each.
6-probes Occlusal Test - Sternocleidomastoid (Static)
It compares two maximum intercuspation tests, lasting 5 seconds each. Moreover, a cervical rotation test - both right and left - is also performed.
6-probes Occlusal Test - Trapezius (Static)
It compares two maximum intercuspation tests, lasting 5 seconds each. Moreover, a shoulder elevation test - both right and left - is also performed.
Chewing Test
It allows to evaluate the neuromuscular coordination in dynamic conditions, i.e. during the masticatory act.
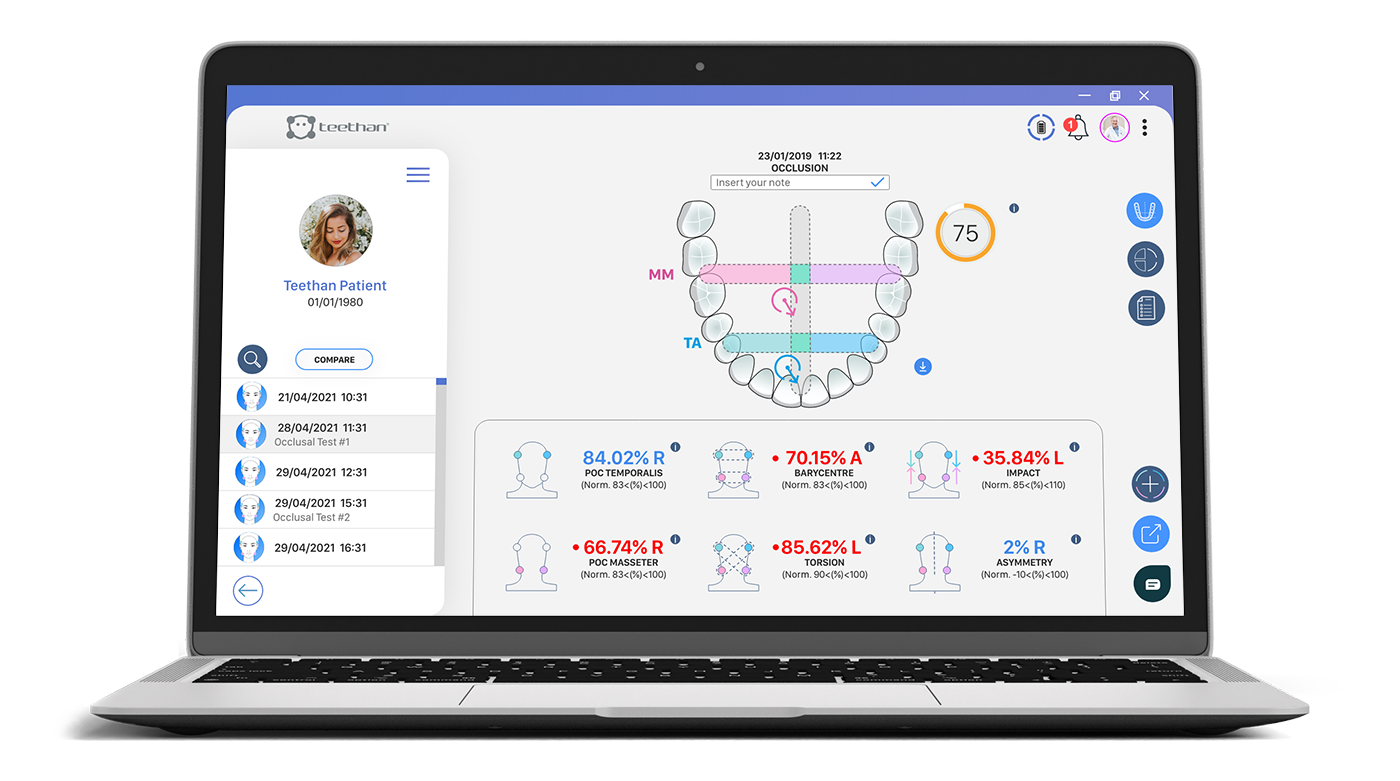
4-PROBES OCCLUSAL TEST
STATIC
In order to measure dental occlusion's balance, the patient has to perform two 5-seconds-long clenching tests. The first is performed using cotton rolls, the second without. Test is completed after the two clenches. Then, an easy-to-interpret report is generated. The test can be easily repeated as it takes just few minutes each time. From the examination we obtain 5 main indices useful for the analysis of the occlusal state. For each index, the relative normality band is available:

Percent overlapping coefficient - POC
Given for each muscle pair, it identifies the overall activity of the temporalis and masseter specifying the side of the muscle that prevails within the pair. It allows to evaluate the overall activity of the muscles as well as to understand the muscle that works more within the pair.

Barycentre - BAR
It compares temporalis activity with masseters activity revealing which, among the two, prevails. Physiologically, a posterior center of gravity is preferred, i.e., where masseters predominate over temporalis.

Torsion - TORS
It assesses the cross activity of the pairs of muscles, revealing the torsional attitude of the mandible in the horizontal plane.

Muscular work - IMPACT
It evaluates the intensity of muscle work of analyzed muscles, returning a parameter closely related to the strength of the bite. A very high work is an indication of a clenching patient, a very low one reveals the presence of nociceptive pain. Knowing the extent of muscle work is also particularly interesting for the research of the correct vertical dimension of the patient.

Asymmetry - ASIM
It compares the activity of right-sided muscles with left-sided muscles indicating any symmetry and allows identification of the dominant side on the patient's occlusal plane.
6-PROBES OCCLUSAL TEST
STATIC
In addition to the assessment of occlusal balance of the 4-probes Occlusal Test, this protocol also allow the investigation of the influence of tooth contact on cranio-cervical neuromuscular balance. In the case of the 6-probes Occlusal Test with sternocleidomastoid, at the end of the second clenching test, the patient must perform cervical rotations both right and left. On the other hand, if one is interestd in trapezius muscle activity, the the patient is required to perform shoulder elevation on both sides.

Percent overlapping coefficient - POC
Given for each muscle pair, it identifies the overall activity of the temporalis and masseter specifying the side of the muscle that prevails within the pair. It allows to evaluate the overall activity of the muscles as well as to understand the muscle that works more within the pair.

Barycentre - BAR
It compares temporalis activity with masseters activity revealing which, among the two, prevails. Physiologically, a posterior center of gravity is preferred, i.e., where masseters predominate over temporalis.

Torsion - TORS
It assesses the cross activity of the pairs of muscles, revealing the torsional attitude of the mandible in the horizontal plane.

Muscular work - IMPACT
It evaluates the intensity of muscle work of analyzed muscles, returning a parameter closely related to the strength of the bite. A very high work is an indication of a clenching patient, a very low one reveals the presence of nociceptive pain. Knowing the extent of muscle work is also particularly interesting for the research of the correct vertical dimension of the patient.

Asymmetry - ASIM
It compares the activity of right-sided muscles with left-sided muscles indicating any symmetry and allows identification of the dominant side on the patient's occlusal plane.

Cervical percent overlapping coefficient - POC SCM/TRA
As with masticatory muscles, it identifies the overall activity of the sternocleidomastoid or trapezius muscles by specifying the side of the muscle that prevails within the pair. It allows to evaluate the overall activity of the muscles and to understand the muscle that works more in the couple.

Cervical load - CL
It expresses the percentage of co-contraction of the sternocleidomastoid or trapezius muscles during the clamping test, that is, when the patient overloads the muscles of the cervical area.
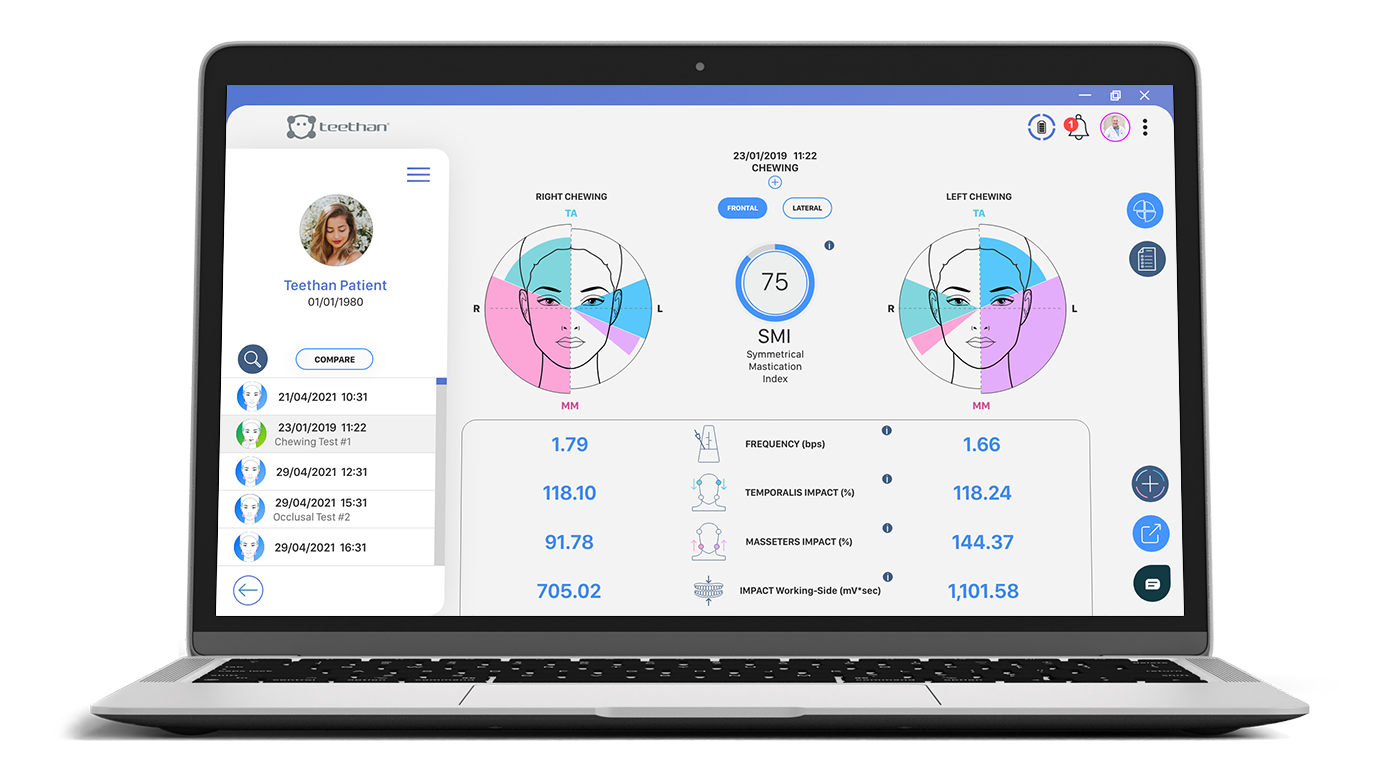
CHEWING TEST
DYNAMIC
It allows to evaluate the neuromuscular coordination in dynamic condition, that is during the chewing act. The test involves two trials of 15 seconds each, performed by a chewing gum, involving first the right side and then the left side of the mouth. From the analysis of the tests, the following indices are considered:

Symmetrical Mastication Index - SMI
It compares the neuromuscular coordination in the two tests. The optimal value is 100%, the further we deviate from it, the greater the masticatory uncoordination.

Chewing frequency
It evaluates the number of chewing acts per second.

Impact
It evaluates work produced by temporalis and masseters during chewing cycles performed on the right side first, and then on the left side. Not normalized impact of the working side is also reported.