Parafunctions: bruxism and dental occlusion
30 October 2021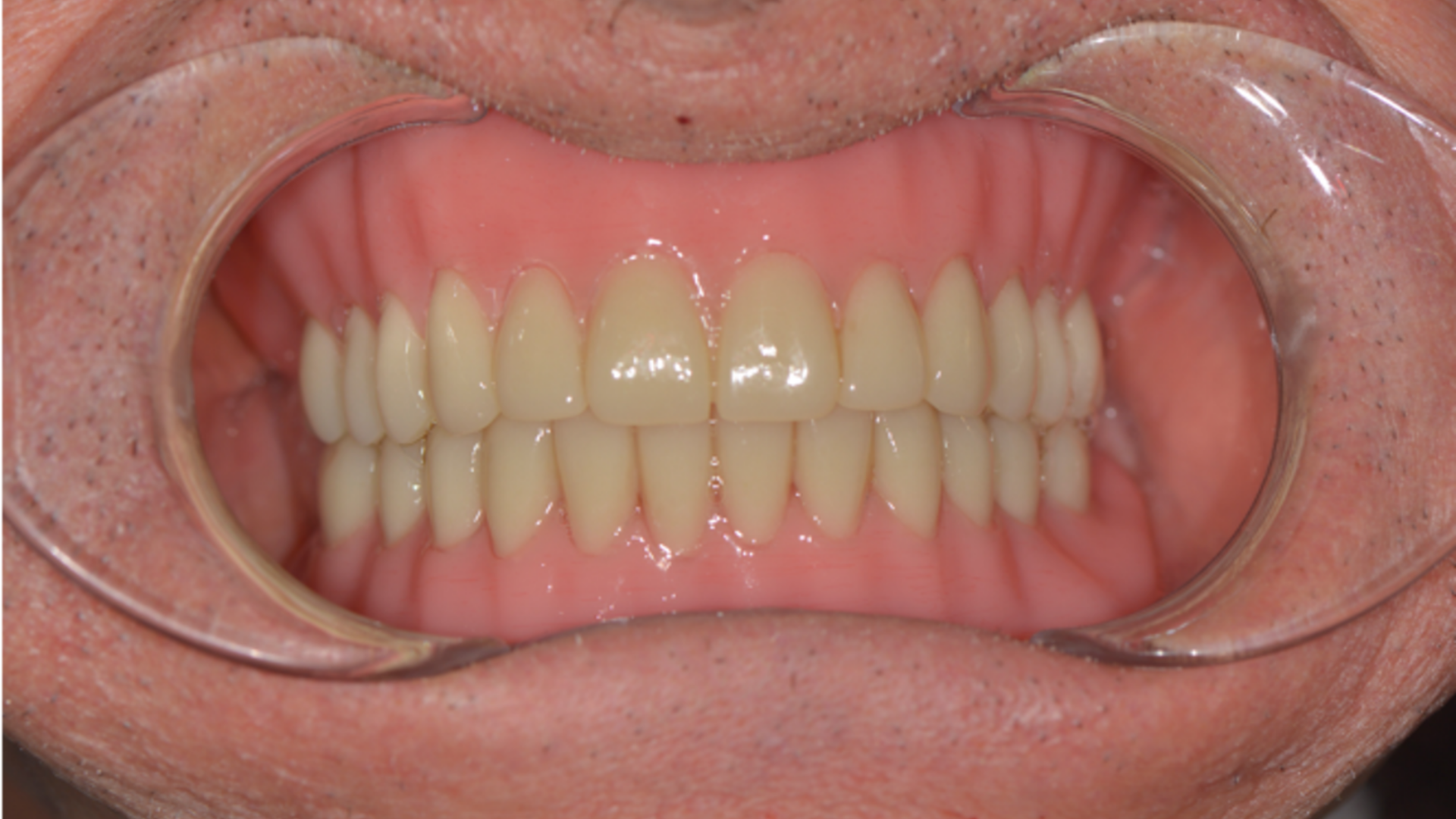
DVO assessment with Teethan: successful tool in the digital workflow of large implant rehabilitations
21 November 2021Case presentation
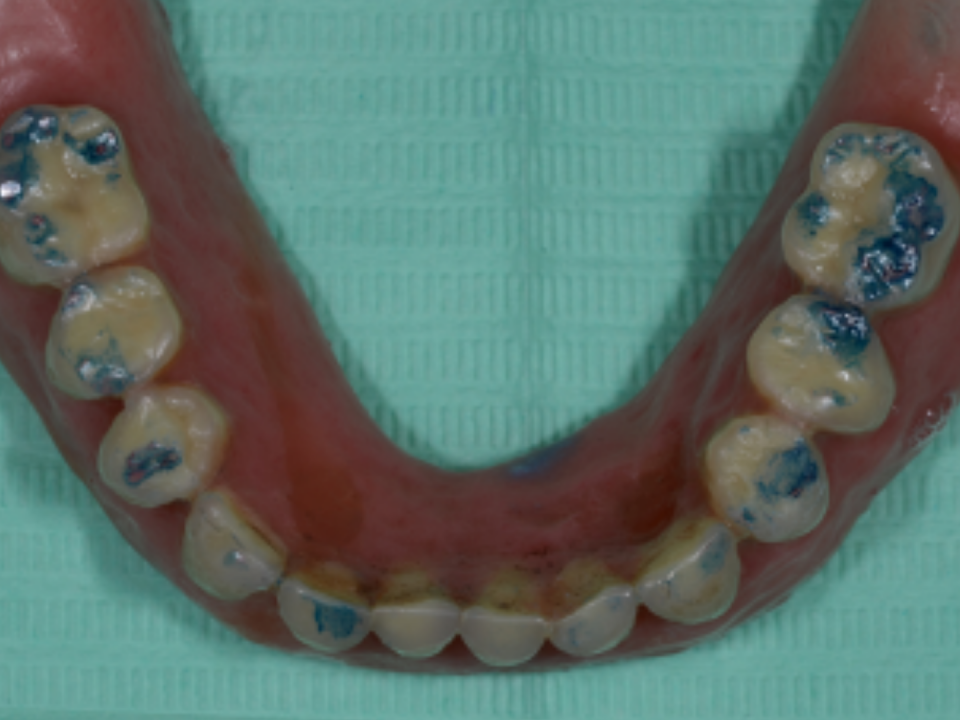
A 57-year-old patient in good general health and nonsmoker is presented. The patient complained a severe aesthetic problem when smiling. Through objective examination, a fixed metal-ceramic total denture supported by abutments that were infiltrated and decayed was evident.There stumps were even more visible due to the presence of a horizontal gingival recession caused by the persistence of a widespread periodontal disease: their conditions were such as not to allow any attempt of recovery and needed to be extracted. Similarly, the support stumps of the prosthesis in the left lower arch had lost their support function in the rehabilitation phase.

Treatment
Not having yet available the Teethan technology, we proceed with the facial and muscular analysis. We find:- A symmetry between right and left side
- A coincidence of the interincisal lines
- Incisive guides and correct canine guides
- An adequate Spee curve
- Absence of pain on direct palpation of the masticatory muscles to exclude possible tension form the pterygoid muscles
- Validated prosthesis
- Adequate Wilson curve
- Opening and closing without pain or clicks
- Investigation of facet wear or other situations affecting the prosthesis such as nocturnal habits (bruxism, clenching, possible fatigue in the morning or upon awakening) gives negative results.
Digital and analog technologies were used, using a facebow the occlusal relationship was transferred to a semi-individual articulator to try and preserve the patient’s occlusal plane and vertical dimension.

Close view of the endo-periodontal condition

Prosthetic stumps in an evident state of decay

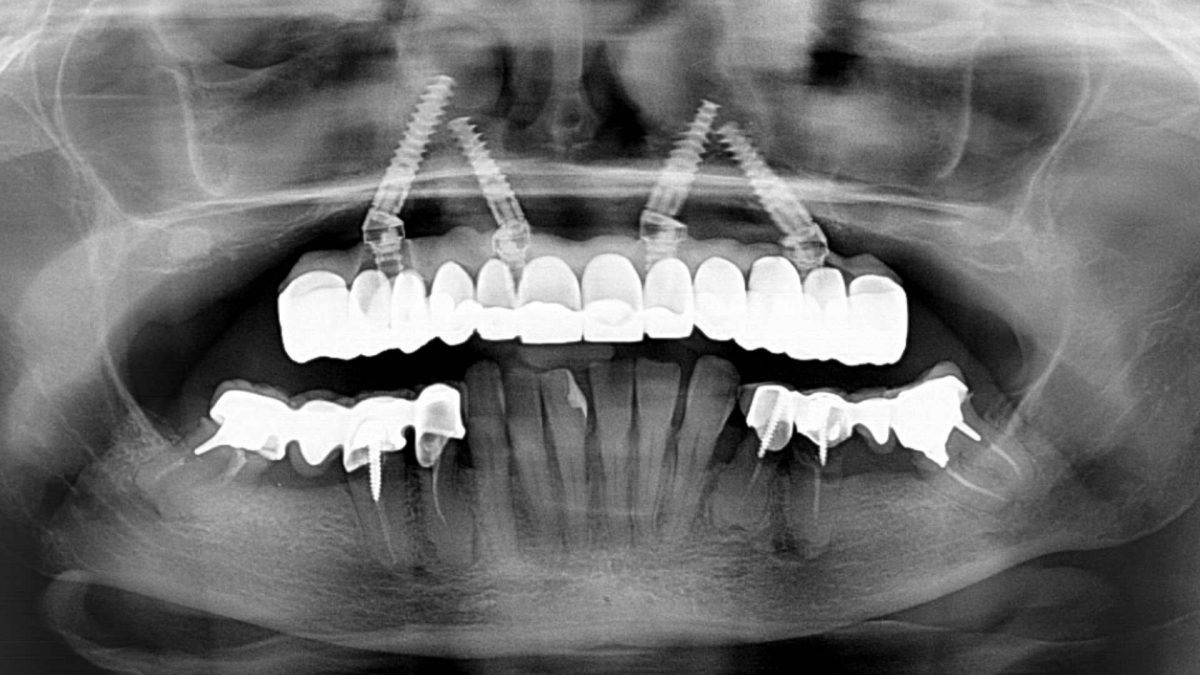
Evaluation with cone beam: the residual bone is reduced in height and there is no bone available beyond the apex of the roots. Orthogonal positioning becomes complicated. Also, the canines are particularly large and occupy the canine fossa area
Surgical treatment
It is thus decided to plan a surgical protocol, using four inclined implants (two anterior and two posterior) according to the Graves and Jensen protocol, called M-Four.



Synthesis of the surgical phase:
Flap exposure: we note the scarce quantity of bone available for the orthogonal positioning of the implants;
Positioning of the four inclined implants: even if the torque index would have allowed an immediate load, we preferred to start a protocol of rigid preservation and socket preservation to try and maintain the initial volumes.
Post-surgical treatment

Control overview; notice the four 16 mm and 18 mm long implants according to the M-Four protocol.

At 4 months the uncovering of the prosthetic abutments is performed: the tissue condition is excellent, and the prosthetic rehabilitation follows.


Circular prosthesis with zirconia frontal elements and composite posterior elements.


Prosthesis directly put in the mouth (left); occlusal control (right).

Control overview, June 2018. You can see the condition of the implants, the condition of the prosthesis (the lower one about to collapse).
New surgical treatment
In November 2018, a new surgery is performed: root extraction, placement of two tilted implants and a zirconia prosthesis.
Teethan exam (1)



The first Teethan examination was performed a few months after delivery of the prosthesis to evaluate the response of the masticatory muscles after rehabilitation. The first examination shows a balance of 89%. POC, temporal, masseter, posterior barycenter and torsion values are perfectly within the norm.
It can be concluded that the occlusal plane the patient had before rehabilitation was the correct one and did not require modifications.
The evaluation of the distribution of temporal and masseter muscles showed their correct function with their areas of action within their respective frameworks; the symmetry index was 3.97% to the left.
It can be concluded that the occlusal plane the patient had before rehabilitation was the correct one and did not require modifications.
The evaluation of the distribution of temporal and masseter muscles showed their correct function with their areas of action within their respective frameworks; the symmetry index was 3.97% to the left.
Reopening of the clinical case
After a few months, the patient requests an aesthetic modification of her anterior frontal group, desiring longer central and lateral incisors.
New prosthetic treatment
The frontal portion is disassembled and replaced from canine to canine and the posterior part is partially modified without altering the vertical dimension of the prosthesis.


Teethan exam (2)
During the trial, immediately prior to delivery, articulation maps are used to adjust the occlusal plane using the Teethan electromyographic control. Thus, we go from occlusion 1 to occlusion 5.


We can see that in both conditions the temporalis POC has a value in the normal range; the masseter in occlusion 1 is slightly more active and therefore the intention is to modify it; the center of gravity in occlusion 1 passes from anterior to posterior in occlusion 5 while the torsion remains on the left with an average value of 86, the impact goes from 66.01% in occlusion 1 to 76.22% in occlusion 5. The symmetry goes from 7.85% on the right side in occlusion 1 to 5.34% on the right side in occlusion 5.
Considering that an optimal condition has been reached, the result obtained in trial 5 is accepted and the work is handed over to the patient.
Same prosthesis: before modifications in July 2018 and after in October 2019.
Considering that an optimal condition has been reached, the result obtained in trial 5 is accepted and the work is handed over to the patient.
Same prosthesis: before modifications in July 2018 and after in October 2019.

July 2018

October 2019
Teethan exam (3) – 3 days later
After 3 days from delivery, the patient was called back to re-evaluate if the torsion recorded in test 5 had changed. Teethan examination was re-examined, and it was noted that the overall balance had increased from 85% to 89% without any intervention on the prosthesis; the POC of the temporalis had decreased slightly from 87% to 86%; the POC of the masseter had increased from 81% to 86%; the center of gravity had changed from posterior to anterior; the torsion had changed from 86.22% on the right side to a balance of 90%; the impact had increased from 76% to 97%. These results are surprising because they were obtained after the delivery of the machine and without any new modifications.



Teethan examination of 14/10/2019, compared to that of 11/10/2019, shows that in the presence of good occlusal plane, how the system has autonomously readjusted itself and with the barycenter that from posterior has become anterior and the temporal and masseter muscles have rebalanced being perfectly contained within their respective areas of action.
Follow-up – 3 years later
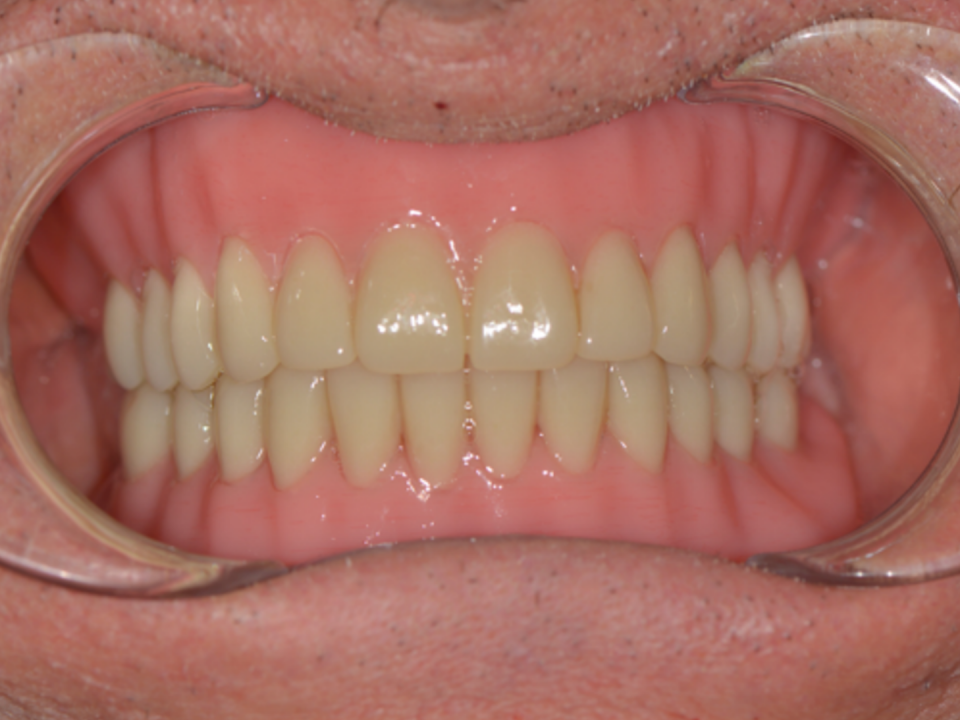
The patient was checked on in April 2021 with Teethan; the occlusal photo shows the posterior elements in composite and the anterior ones in zirconia. The occlusal planking is intact: there are no wear veneers, no areas of injury, and the patient has never worn any type of nocturnal device.


The left lower arch is made up of bridges and implants, except for the frontal group that is represented by the patient’s dentition and therefore the function of periodontal receptors is there, but it is not effective as it would be in a complete natural dentition.

Picture of the lower arch: the zirconia bridge from the left side and the prosthesis that will soon be replaced.
Teethan exam (4)

A further Teethan examination is performed two and a half years later the last checkup; the overall index is reduced to 85%, the center of gravity has remained anterior; the impact has lowered.

In the direct comparison between 2019 and 2021 it is seen that the masticatory and muscular picture remained unchanged: the temporal POC from 86% increased to 88%; the masseter from 86.28% to 86.57% and the temporal POC did not increase also because the center of gravity became more anterior, the impact lowered from 96.19% to 66.87%.
The patient is asked if she experiences any masticatory discomfort. As she doesn’t, it is decided not to intervene on the impact.
The patient is asked if she experiences any masticatory discomfort. As she doesn’t, it is decided not to intervene on the impact.


Teethan examination is important for muscle function: the temporal muscles work more but in a symmetrical way as well as the function of the masseter muscles in the lower zone. Also, the percentage distribution is smaller, and the asymmetry has a value of 0.84% slightly to the right.

The radiographic examination is important for those who do implantology and surgery, a remote control of the work performed aims to evaluate the state of integration of the implants and the general conditions of the rehabilitation. Despite the compromised initial skeletal conditions, through the M-four protocol and thanks also to the balancing of the occlusal plane though the control operated by Teethan, these technologies allowed us to express judgments of predictability to guarantee the work of the clinician and patient satisfaction.