Contact us at alifix@teethan.com and one of our ALIFIX-experienced dentists will answer you.
ALIFIX is a medical device which, thanks to its particular design, fits comfortably between the teeth. It induces a gentle training that relaxes masticatory and neck muscles during physiologically frequent movements of swallowing.
ALIFIX, makes it possible to check the correct balance of the muscles of mastication, through the application of simple and repeatable clinical protocols.
Assessing the mastication act is an increasingly useful procedure to check whether tooth contacts and muscles are in balance with each other.
A condition of imbalance - which is often clinically silent - can interfere with the finalization and stability of dental or orthodontic treatment. It can also cause increased occlusal sensitivity in the patient.
ALIFIX allows to test the chewing act: it temporarily deconditions muscles to bring to light possible pre-contacts and detects the correct position of the jaw.
CLINICAL ASSESSMENT MEETS INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS
In the medical field, instrumental examinations accompany clinical assessment to support measure. The combination of these two kinds of data, clinical and instrumental, is fundamental to make a correct diagnosis: the lack of clinical evaluation makes data difficult to interpret with the risk of non-adequate therapy.
Combining Alifix and Teethan, we can obtain a complete and more accurate diagnosis by selectively investigating the activity of the Temporalis and Masseter muscles during clenching, swallowing and the chewing act.
The presence of a muscular imbalance is not always evident as it is often concealed by the patient's ability to adapt. In asymptomatic cases, it is the dentist's due to search for imbalances.
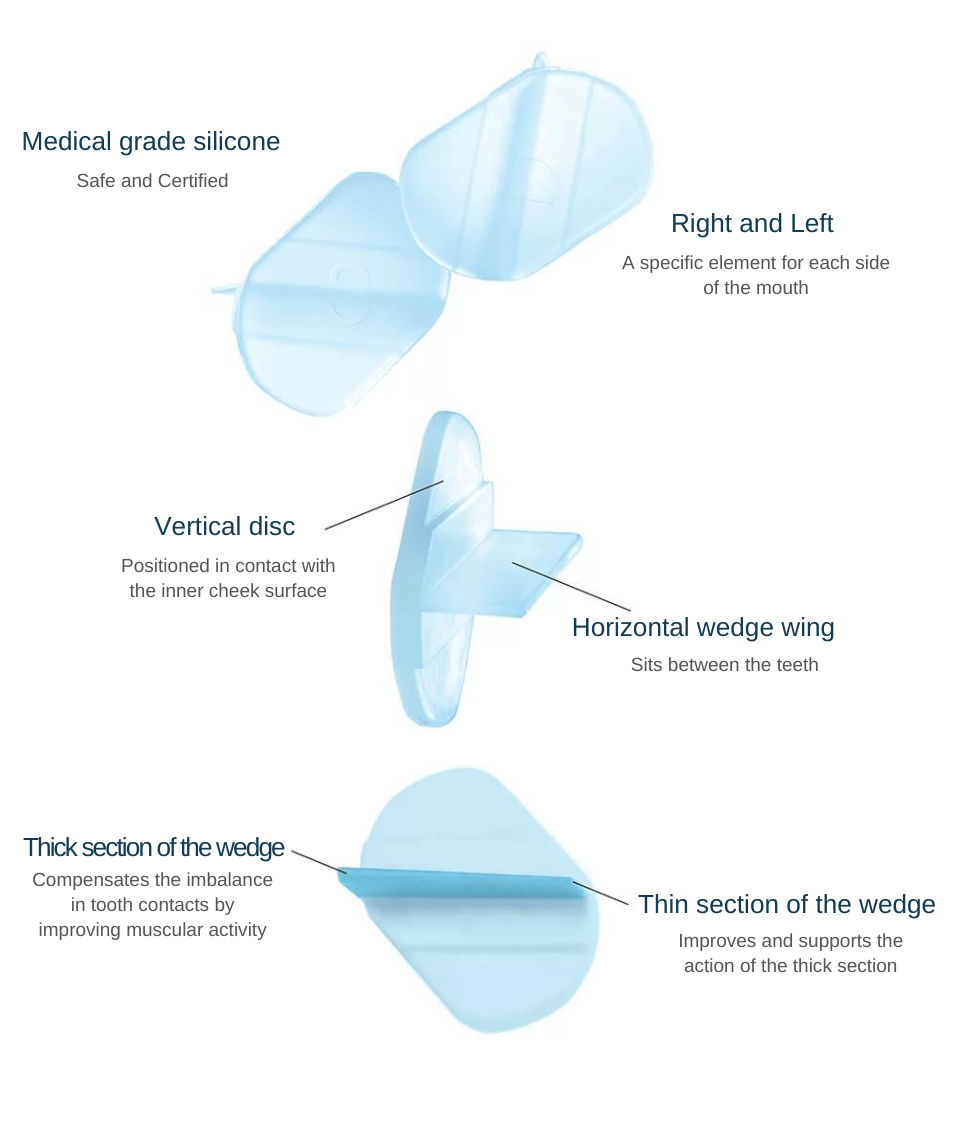
Thanks to its wedge-shaped design, ALIFIX is able to compensate the occlusion alterations, to deprogram and temporarily re-balance the action of Temporalis and Masseter. This ALIFIX’s ability can be monitored with Teethan.
ALIFIX does not interfere the practitioner's normal procedures because it can be easily integrated.
DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY
The clinical analysis carried out with ALIFIX includes three tests that analyze the Temporal and Masseter, as Teethan does:
- Comfortable position test: assesses the balance of muscles and dental contacts;
- Fatigue test: identifies "occlusal-sensitive" subjects;
- Lateral disequilibrium test: indicates unbalanced chewing habits;

OPERATING PROTOCOL 1
All tests should be performed with the patient seated on the dental unit stool and without resting the back on the chair.
Comfortable position test: assessing the balance of muscles and dental contacts.
What is the purpose
It allows to detect an imbalance of the Masseter and Temporalis and to correlate it with the presence of incorrect dental contacts or alterations in the Vertical Dimension. This information guides its correction.
When it is useful
For each change that is made to the occlusion, like fillings, traditional or implant prosthetic reconstructions (particularly in the provisional phase), orthodontic treatments.
How to do it
(right and left ALIFIX elements are used simultaneously)
- Carry out the basic test with Teethan (5 seconds of cotton rolls calibration an d5 seconds of clenching in maximum natural intercuspation)
- Insert ALIFIX in both sides with the thickest wedge posteriorly. Have the patient chew and swallow once or twice. Ask the patient if he feels comfortable
- Perform another Teethan test, keeping ALIFIX in the mouth - thickest wedge posteriorly
- Repeat these steps with the thicker part of the wedge anteriorly. Have the patient chew and swallow once or twice. Ask the patient if he feels more comfortable in this position or in the previous one. Take note of the result on the MUSCULAR CHART.
- Perform the Teethan test, keeping ALIFIX in the mouth - greater thickness in front
In a balanced situation the patient does not perceive any differences between anterior or posterior wedge position and there are no remarkable changes in the data provided by Teethan.
The comfortable position of the wedge, anterior or posterior, is related to a precise muscular imbalance associated with a specific alteration of the dental contact.
OPERATING PROTOCOL 2
All tests should be performed with the patient seated on the dental unit stool and without resting the back on the chair.
Fatigue test: quantifying the level of fatigue of the temporalis and masseter muscles.
What is the purpose
It’s helpful in identifying patients with reduced adaptive capacity ("occlusion-sensitive"). Muscle fatigue is often present even in asymptomatic - apparently healthy - subjects and determines a reduction in the patient's ability to adapt to occlusal changes.
When it is useful
Firstly, when Teethan’s disequilibrium data do not change (or even worsen) during the comfortable position test. It can be used, also, whenever the patient clenches in different ways or when he "cannot adapt" to changes in occlusion ("occlusion-sensitive" patient).
How to do it
(Left and right Alifix elements are used simultaneously)
- Insert Alifix from both sides with the thicker element in the most comfortable position.
- Chew gently until the first feeling of tiredness or muscle discomfort appears.
- Write down on the MUSCULAR CHART the time and the muscle(s) showing the first signs of fatigue.
Normally, you can chew for up to 5 minutes.
If the tiredness is reported before that time (in several cases, resistance is barely 20-30 seconds), it means that the muscles are affected by fatigue and that they should be trained with a personalized protocol. Furthermore, if the sensation is reported only on one side, a functional asymmetry is to be taken into account.
OPERATING PROTOCOL 3
All tests should be performed with the patient seated on the dental unit stool and without resting the back on the chair.
Lateral disequilibrium test: identifies the presence of potentially harmful habits.
What is the purpose
It highlights muscles’ asymmetrical use, which may be the cause of functional joint or dental overload.
When it is useful
When there is asymmetrical dental support (e.g. cross-bite, functional mandibular deviations, asymmetrical wear of prostheses). This may favor both unilateral muscular activity and chewing habits, that are maintained after the restoration of the new occlusion.
How to do it
(Unilateral use: the right and left Alifix elements are used individually to assess the function of each side)
- Place Alifix on the right side with the thickest wedge in the anterior position
- Perform the right chewing test with Teethan.
- Observe if the chin moves to the same side of chewing.
- Remove right-side Alifix and place the left-side one with the thicker wedge in the anterior position.
- Repeat the same evaluation with Alifix and Teethan on the left side.
- Observe if the chin moves to the same side of chewing.
- Report data on the MUSCULAR CHART
When chewing on the right side, the chin moves mainly to the right and vice versa. If the chin always moves to the same side, whether the patient is chewing on the right or on the left, there is a muscular imbalance which must be corrected with planned training.
Contact us at alifix@teethan.com and one of our ALIFIX-experienced dentists will answer you.

